Cybersecurity researchers are warning of a suspected exploit of a recently discovered critical security flaw in the Apache ActiveMQ open-source message broker service that could result in remote code execution.
“In both cases, the adversary attempted to deploy ransomware binaries on target systems in an effort to extort money from victim organizations,” cybersecurity firm Rapid7 revealed in a report published Wednesday.
“Based on the ransom note and available evidence, we attribute this activity to the HelloKitty ransomware family, the source code of which was leaked on a forum in early October.”
The intrusion is said to involve the exploitation of CVE-2023-46604, a remote code execution vulnerability in Apache ActiveMQ that allows a threat actor to run arbitrary shell commands.
It is worth noting that the vulnerability has a CVSS score of 10.0, which represents maximum severity. This has been addressed in ActiveMQ versions 5.15.16, 5.16.7, 5.17.6, or 5.18.3 released late last month.
The vulnerability affects the following versions –
- Apache ActiveMQ 5.18.0 before 5.18.3
- Apache ActiveMQ 5.17.0 before 5.17.6
- Apache ActiveMQ 5.16.0 before 5.16.7
- Apache ActiveMQ before 5.15.16
- Apache ActiveMQ Legacy OpenWire Module 5.18.0 before 5.18.3
- Apache ActiveMQ Legacy OpenWire Module 5.17.0 before 5.17.6
- Apache ActiveMQ Legacy OpenWire Module 5.16.0 before 5.16.7
- Apache ActiveMQ Legacy OpenWire Module 5.8.0 before 5.15.16
Since the bugs’ disclosure, a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code and additional technical specifics have been made publicly available, with Rapid7 noting that the behavior it observed in the two victim networks is “similar to what we would expect from exploitation of CVE-2023-46604.”
After successful exploitation the opponent tries to load remote binaries named M2.png and M4.png using Windows Installer (msiexec).
Both the MSI files contain a 32-bit .NET executable named dllloader that, in turn, loads a Base64-encoded payload called EncDLL that functions akin to ransomware, searching and terminating a specific set of processes before commencing the encryption process and appending the encrypted files with the “.locked” extension.
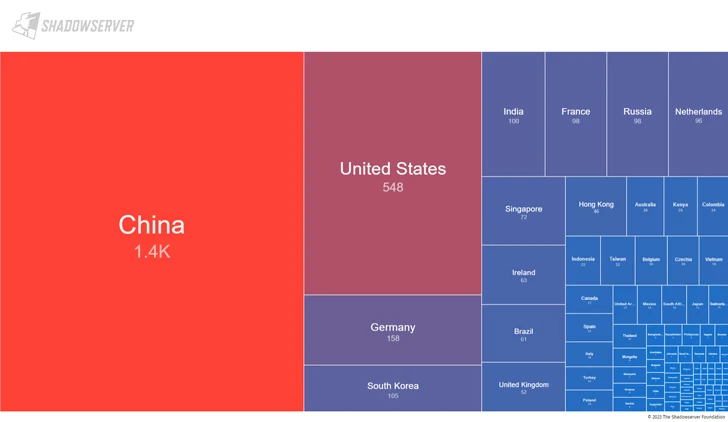
The ShadowServer Foundation said it found 3,326 internet-accessible ActiveMQ instances as of November 1, 2023 that are susceptible to CVE-2023-46604. Most of the vulnerable servers are located in China, USA, Germany, South Korea and India.
In light of active exploitation of the flaw, users are advised to update to the fixed version of ActiveMQ as soon as possible and scan their networks for indicators of compromise.
