State-sponsored threat actors from the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) have been found targeting blockchain engineers of an anonymous crypto exchange platform via Discord with a new macOS malware called KANDYKORN.
Elastic Security Labs, citing an analysis of the network infrastructure and techniques used, said the April 2023 activity shows overlap with the notorious adversary collective Lazarus Group.
“Threat actors lured blockchain engineers with Python applications to quickly gain access to the environment,” security researchers Ricardo Ungureanu, Seth Goodwin and Andrew Pease said in a report published today.
“This intrusion involved several complex steps each of which intentionally used defense evasion techniques.”
This is not the first time the Lazarus Group has leveraged macOS malware in its attacks. Earlier this year, the threat actor was observed distributing a backdoored PDF application that culminated in the deployment of RustBucket, an AppleScript-based backdoor capable of retrieving a second-stage payload from a remote server.
What makes the new campaign special is that the attacker impersonates blockchain engineers on a public Discord server, using social engineering to trick victims into downloading and executing a ZIP archive containing malicious code.
“The victims believed they were installing an arbitrage bot, which is a software tool capable of profiting from cryptocurrency rate differences between platforms,” the researchers said. But in reality, a series of attacks led to the delivery of KANDYKORNs after a five-step process.
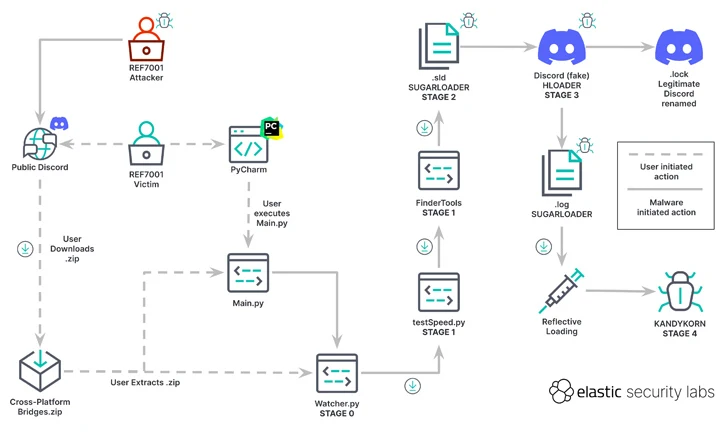
“KANDYKORN is an advanced implant with various capabilities to monitor, communicate, and avoid detection,” the researchers said. “It uses reflective loading, a direct-to-memory form of execution that can bypass detection.”
The starting point is a Python script (watcher.py), which retrieves another Python script (testSpeed.py) hosted on Google Drive. On the other hand, this dropper fetches another Python file from the Google Drive URL, named FinderTools.
FinderTools also functions as a dropper, downloading and executing a hidden second stage payload referred to as SUGARLOADER (/Users/shared/.sld and .log) that ultimately connects to a remote server in order to retrieve KANDYKORN and execute it directly in memory.
SUGARLOADER is also responsible for launching a Swift-based self-signed binary known as HLODAER that attempts to pass off as the legitimate Discord application and executes .log (i.e., SUGARLOADER) to achieve persistence using a method called execution flow hijacking.
KANDYKORN, which is the payload of the final stage, is a full-featured memory resident RAT with built-in capabilities to enumerate files, run additional malware, exfiltrate data, terminate processes, and run arbitrary commands.
“The DPRK, through entities such as the Lazarus Group, continues to target crypto-industry businesses with the goal of stealing cryptocurrencies in order to circumvent international sanctions that hinder the development of their economy and ambitions,” the researchers said.”
Kimsuky resurfaces with updated FastViewer malware
This revelation comes after the S2W Threat Analysis team revealed an updated version of Android spyware called FastViewer, which is used by North Korean threat group Kimsuki (aka APT43), an affiliate hacking organization of Lazarus Group.
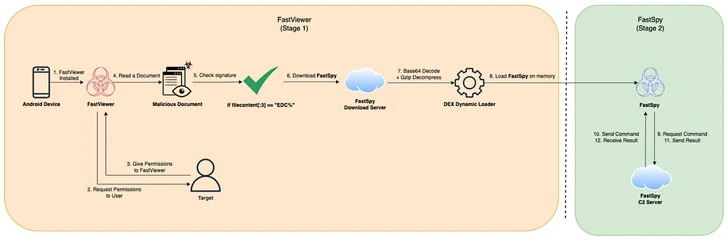
FastViewer, first documented by the South Korean cybersecurity firm in October 2022, abuses Android’s accessibility services to covertly harvest sensitive data from compromised devices by masquerading itself as seemingly harmless security or e-commerce apps that are propagating via phishing or smishing.
It is also designed to download a second stage of malware called FastSpy, which is based on the open-source project Androspy, to execute data collection and exfiltration commands.
“The variant has been in production since at least July 2023 and, like the early version, induces installation by distributing repackaged APKs that incorporate malicious code into legitimate apps,” S2W said.
A notable aspect of the new version is the integration of FastSpy functionality into FastViewer, eliminating the need to download additional malware. S2W said, “There are no known cases of this variant being distributed in the wild.”
