While IT security managers in companies and public administrations rely on the concept of Zero Trust, APTS (Advanced Persistent Threats) are putting its practical effectiveness to the test. Analysts, on the other hand, understand that Zero Trust can only be achieved with comprehensive insight into one’s own network.
More recently, several government agencies were targeted in an attack believed to have been carried out by the Chinese hacker group Storm-0558. They used forged digital authentication tokens to access webmail accounts running on Microsoft’s Outlook service. In this incident, the attackers stole a signing key from Microsoft, enabling them to issue functional access tokens for Outlook Web Access (OWA) and Outlook.com, and download emails and attachments. Due to a plausibility check error, the digital signature, which was only for personal customer accounts (MSAs), also worked in Azure Active Directory for business customers.
Embracing the Zero Trust Revolution
According to a report by vendor Okta (State of Zero-Trust Security 2022), 97% of respondents are already engaged in a zero-trust strategy or plan to implement it within the next 18 months. This has increased the percentage of Zero Trust advocates from 24% (2021) to 55% (2022). The security model known as zero trust is a comprehensive security strategy designed to continuously audit and verify access to resources, both internally and externally. Many organizations are adopting this security strategy based on the principle that network devices and users must continually prove their identity, as they are not automatically trusted.
Zero Trust relies on continuous monitoring and dynamic control for applications, users, and devices. This limits access to resources to a minimum and all identities on the platform are assessed using the same criteria as hosts. The overarching goal is to increase security by granting access only to those who continually prove their identity and whose behavior is continually scrutinized.
Peeking Beyond the Perimeter: What’s Really Happening in Your Network
Identity and Access Management (IAM) undoubtedly play a fundamental role in Zero Trust. Unfortunately, ongoing verification of users’ identities proves ineffective in cases of stolen identity. Furthermore, attackers can bypass these systems by manipulating meta-information such as the geolocation of potential logins using fake VPN addresses. IDS/IPS systems are tasked with detecting suspicious or unauthorized activity, virus infections, malware and ransomware, zero-day attacks, SQL injection, and more. However, IDS/IPS systems often only detect known signatures, such as previously identified malicious domains or IP addresses. If a domain hasn’t already been flagged as malicious, traditional security solutions can ignore it, allowing attackers to exploit weak links in the chain. As a result, traditional cyber security systems can sometimes falter when it comes to implementing zero trust.
To effectively implement a zero trust security strategy, organizations are increasingly turning to network analysis tools, as recently recommended by analyst firm Forrester (“The Network Analysis and Visibility Landscape, Q1 2023”) Has gone. According to Forrester Reports, security and risk professionals must use network detection and response (NDR) tools to monitor their networks, detect threats, locate applications and assets, and capture malicious data packets. These actions contribute to the effective detection of threats within the IT infrastructure.
Network Detection and Response (NDR): The unsung heroes of Zero Trust Security
NDR solutions are critical to building a flexible and effective zero trust architecture. They provide real-time visibility into network traffic, monitor user behavior and device activity, and enable the rapid detection and response to suspicious network operations or unusual activities. This visibility extends to all operating systems, application servers, and IoT devices.
Forrester highlights that the importance of enterprise networks in cyber attacks is often underestimated. Cyber criminals use fake identities or zero-day exploits to infiltrate corporate networks, then discover targets, gain access to privileged systems, install ransomware or other malware, and spread malware throughout the network Infiltrate the corporate data flow. NDR facilitates internal reconnaissance – where the attacker surveys potential targets – or lateral movement detection when the attacker is already in the network. NDR systems aggregate data from all switches and operate entirely without agents, which may not be installable in many environments.
Machine Learning NDR: The New Standard in Anomaly Detection
With machine learning (ML), network detection and response (NDR) systems are able to detect traffic anomalies without relying on pre-stored, known “indicators of compromise” (IoC). These ML models are designed to be trained continuously, which enables them to detect new threats and attack techniques. This approach significantly speeds up the detection of malicious activities and enables early attack mitigation. In addition, it helps identify unknown, suspicious behavior and reduces the time attackers stay within the network, thereby increasing overall security.
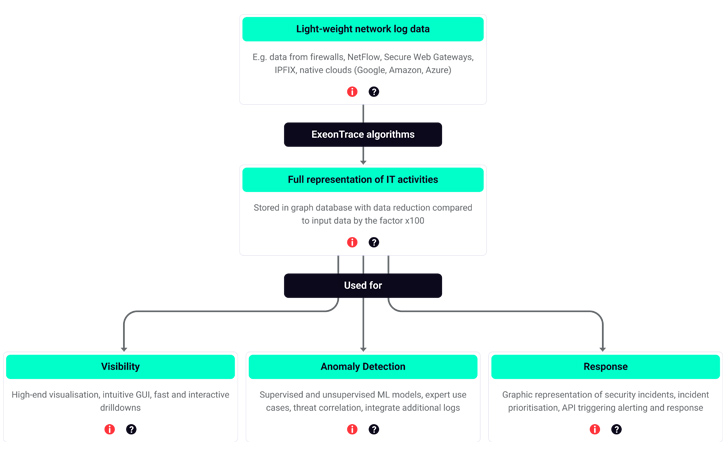
___ How ExeonTrace, a leading ML-based NDR, analyzes meta data to provide network visibility, anomaly detection and incident response.
Machine learning algorithms establish a baseline of normal network behavior by analyzing data and algorithms to learn what is “normal” for a network in communication patterns. These algorithms are trained to learn what is “normal” activity for a network, enabling them to detect deviations from this established baseline. Examples of such deviations include suspicious connections, abnormal data transfer, traffic patterns that are outside established norms, lateral activities within the network, data intrusion, and more.
Exeon is a leading NDR solutions provider headquartered in Switzerland with a strong knowledge base and rooted in cyber security expertise. Exeon Trace, the NDR platform, provides comprehensive network monitoring powered by advanced machine learning technology. It enables automated detection of potential cyber threats, making it an essential tool for Security Operations Center (SOC) teams and Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) looking to implement a robust zero trust security strategy and Committed to maintaining.
